🧩 Understanding 3D Printing
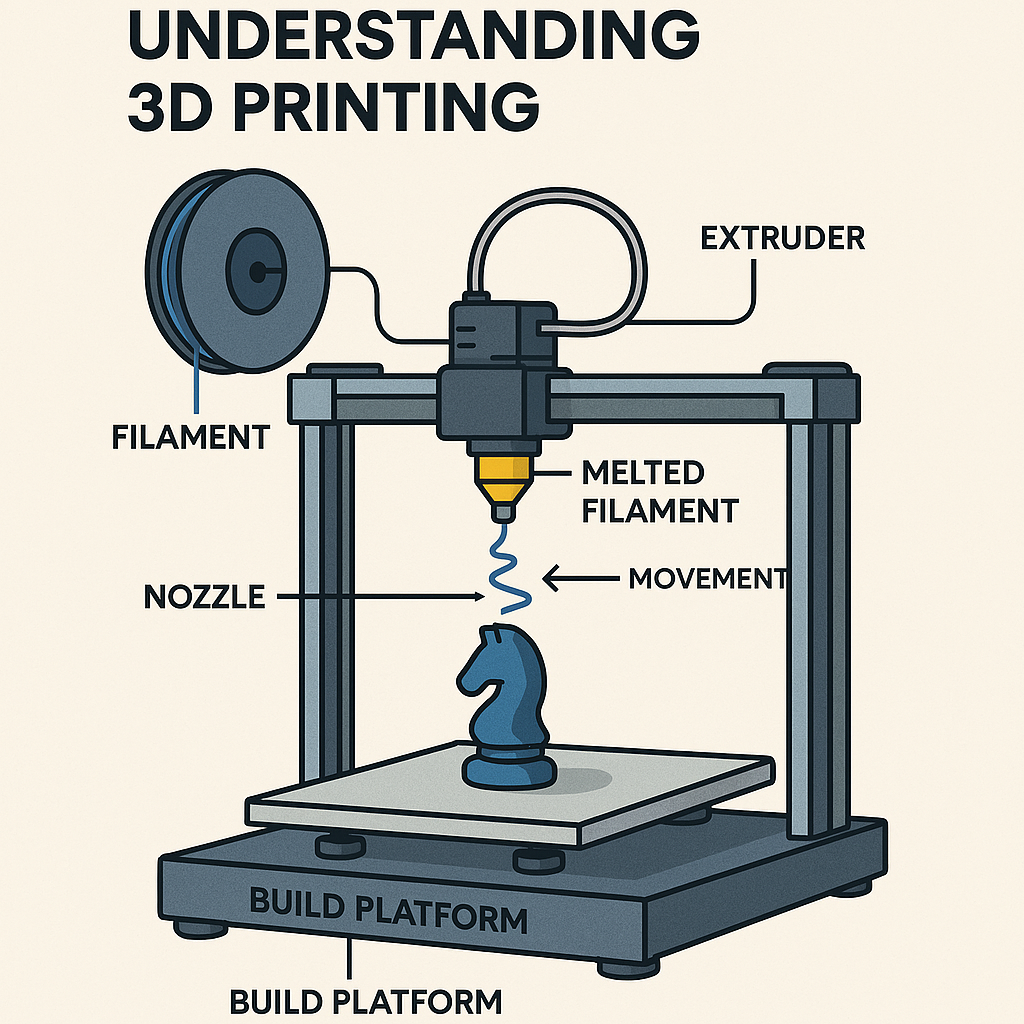
3D printing — also known as additive manufacturing — is a process that builds objects layer by layer from a digital model. The technology began in the early 1980s with the invention of stereolithography, and has since expanded into multiple printing methods used across industries today.
🖨️ How 3D Printing Works
3D printers create objects by depositing or solidifying material one layer at a time. Several major technologies are used:
- 🧵 FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) – melts and extrudes plastic filament
- 🔦 SLA/DLP (Resin Printing) – cures liquid resin with UV light
- ⚡ SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) – fuses powdered material with a laser
Each method offers different strengths depending on detail, durability, and material needs.
🧪 Materials Used in 3D Printing
Modern 3D printing supports a wide range of materials:
- 🌱 PLA – easy to print, biodegradable, great for general use
- 🛠️ ABS – strong, durable, ideal for functional parts
- 🧵 Nylon & TPU – flexible or high‑strength applications
- 🔩 Metals & Ceramics – industrial and engineering use
- 🧬 Bio‑materials – medical and research applications
This versatility allows 3D printing to serve everything from hobby projects to aerospace components.
🚀 Real‑World Applications
3D printing is transforming industries worldwide:
- 🏥 Healthcare – custom implants, prosthetics, surgical models
- 🚗 Automotive & Aerospace – lightweight, complex components
- 🏭 Manufacturing – rapid prototyping and low‑waste production
- 🎨 Consumer Goods & Design – custom products and artistic creations
Its ability to produce intricate shapes quickly makes it a powerful tool for innovation.
🌍 The Future of Fabrication
3D printing continues to evolve, offering greater precision, more materials, and faster production. Its blend of efficiency, customization, and sustainability positions it as a key technology shaping the future of manufacturing and design.
🧭 What Is CAD Design?
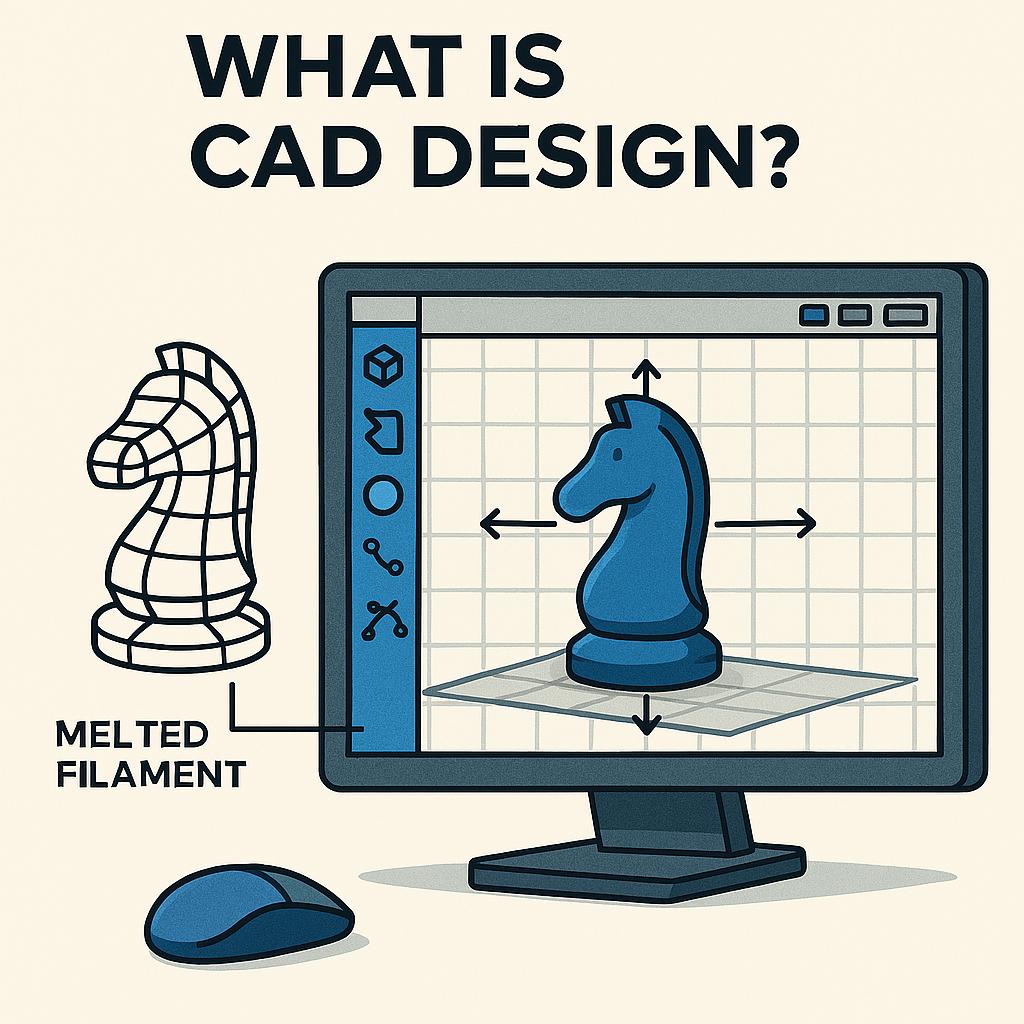
Computer‑Aided Design (CAD) is the digital foundation of modern fabrication. It allows designers, engineers, and makers to create precise 2D and 3D models that serve as the blueprint for both 3D printing and CNC machining. CAD ensures every dimension, angle, and detail is accurately represented long before production begins.
🖥️ Why CAD Matters in Fabrication
CAD software provides the tools needed to design complex parts with accuracy and consistency. These digital models guide the entire fabrication process:
- 📐 Precise Dimensions — every measurement is defined down to fractions of a millimeter
- 🧱 Structural Details — internal geometry, wall thickness, and supports for 3D printing
- 🛠️ Toolpaths for CNC — the CAD model determines how the router moves, cuts, and shapes material
Accurate CAD design directly impacts the quality of the final part, making it essential for both additive and subtractive workflows.
🗂️ CAD Files as Digital Blueprints
CAD files act as the master plan for production:
- For 3D printing, they define shape, size, internal structure, and print‑ready geometry
- For CNC machining, they determine cutting paths, depths, and tool movements
A well‑designed CAD file ensures smooth fabrication, fewer errors, and predictable results.
🧰 Popular CAD Software
Different projects call for different tools. Some of the most widely used CAD programs include:
- 📏 AutoCAD — industry standard for 2D drafting and technical drawings
- 🧩 SolidWorks — powerful 3D modeling with simulation and engineering tools
- 🔧 Fusion 360 — an all‑in‑one platform combining CAD, CAM, and CAE
These platforms support collaboration, version control, and efficient workflows — all crucial for modern fabrication.
🚀 The Role of CAD in Innovation
As fabrication technologies evolve, CAD remains at the center of innovation. It enables rapid prototyping, precise engineering, and seamless integration between digital design and physical production. Whether you’re printing a prototype or machining a final part, CAD accuracy and software proficiency are key to project success.
🔧 Hybrid Fabrication: CNC Routers + 3D Printing + Epoxy
The integration of CNC routers and 3D printing marks a major advancement in fabrication, combining geometric complexity with precision finishing. This hybrid workflow enables designers and engineers to produce components that are both structurally refined and visually striking.
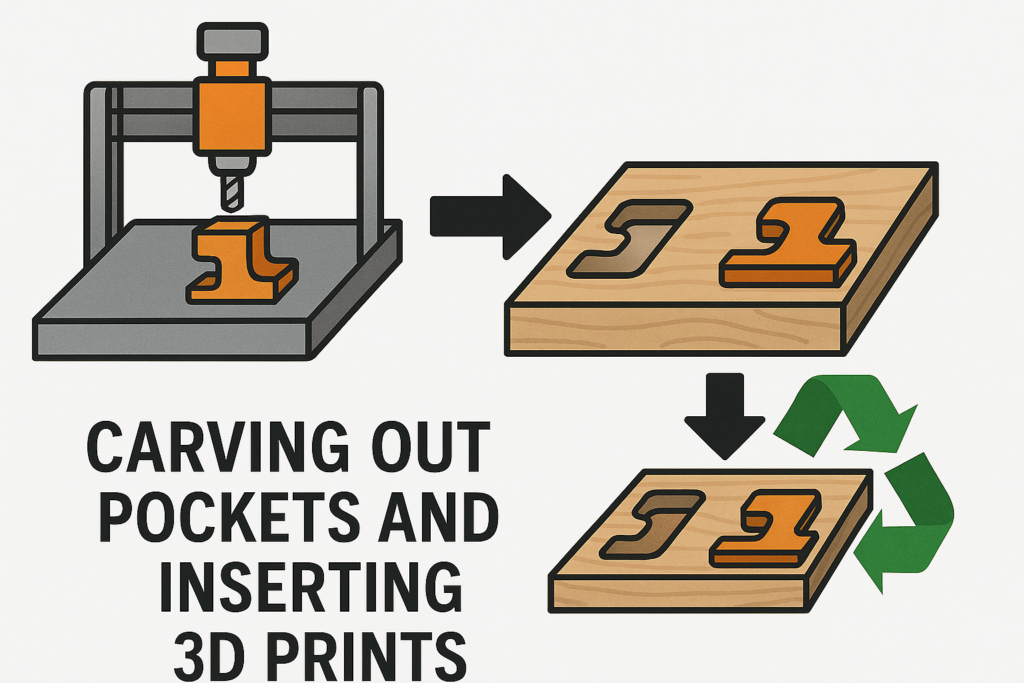
🪵 Step 1: Carve Out Wood Pockets
Using a CNC router, precise pockets are carved into wood, plastic, or composite panels. These recesses are designed to match the geometry of the 3D printed inserts, ensuring a snug fit and clean alignment.
🧩 Step 2: Insert 3D Printed Parts
Custom 3D printed components—logos, joints, decorative elements—are press-fit or bonded into the CNC-carved pockets. This step merges additive and subtractive techniques, allowing for modular, customizable designs.
🧪 Step 3: Fill with Epoxy
Once the inserts are in place, epoxy resin is poured over the surface to encapsulate the assembly. This creates a smooth, durable finish that enhances both aesthetics and structural integrity. Colored or clear epoxy can be used to match branding or design goals.
💡 Why It Works
- Precision: CNC routers deliver tight tolerances and clean edges.
- Complexity: 3D printing enables intricate shapes and internal features.
- Durability: Epoxy seals and protects the final product.
- Versatility: Works with wood, plastics, composites, and printed polymers.
🛠️ Applications
Prototypes with sealed electronicsd CNC Router Project
Custom signage with embedded logos
Furniture inlays and decorative panels
Enclosures with functional inserts
🚀 Getting Started with 3D Printing & CNC Routing
Starting a fabrication project is exciting — and choosing the right tools sets the stage for success. Whether you’re printing, routing, or combining both, the right setup helps you move from concept to finished product smoothly.
🖨️ Choosing the Right 3D Printer
When selecting a 3D printer, consider:
- 📦 Build Volume — determines the maximum size of your parts
- 🎯 Layer Resolution — important for fine details and smooth surfaces
- 🧵 Material Compatibility — PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, and specialty filaments
High‑resolution printers are ideal for projects requiring tight tolerances or intricate geometry.
🪚 Choosing the Right CNC Router
For CNC routing, focus on:
- 📐 Machine Size — ensure it fits your workspace
- 🪵 Material Capability — wood, plastics, composites, or metals
- ⚙️ Rigidity & Accuracy — essential for clean cuts and consistent results
💰 Understanding Project Costs
Budgeting goes beyond the machine purchase. Plan for:
- 🔄 Consumables — filament, router bits, adhesives, finishing supplies
- 🛠️ Maintenance — wear parts, calibration tools
- 💻 Software — CAD/CAM licenses or subscriptions
Planning ahead helps avoid unexpected expenses later.
📦 Sourcing the Right Materials
For 3D Printing
- PLA for general use
- ABS for durability
- PETG for strength and flexibility
- Specialty materials for advanced applications
For CNC Routing
- 🪵 Wood — furniture, signs, decorative work
- 🔶 Plastics — enclosures, prototypes
- 🔩 Metals — high‑strength components
Local suppliers and trusted online stores make it easy to get what you need.
🤝 Need Professional Help?
If you want expert support with design, machining, or production, we’re here to help. Our services streamline your workflow and ensure precision from start to finish — so you can stay focused on the creative side of your project.utable online stores can provide everything you need to bring your ideas to life.
